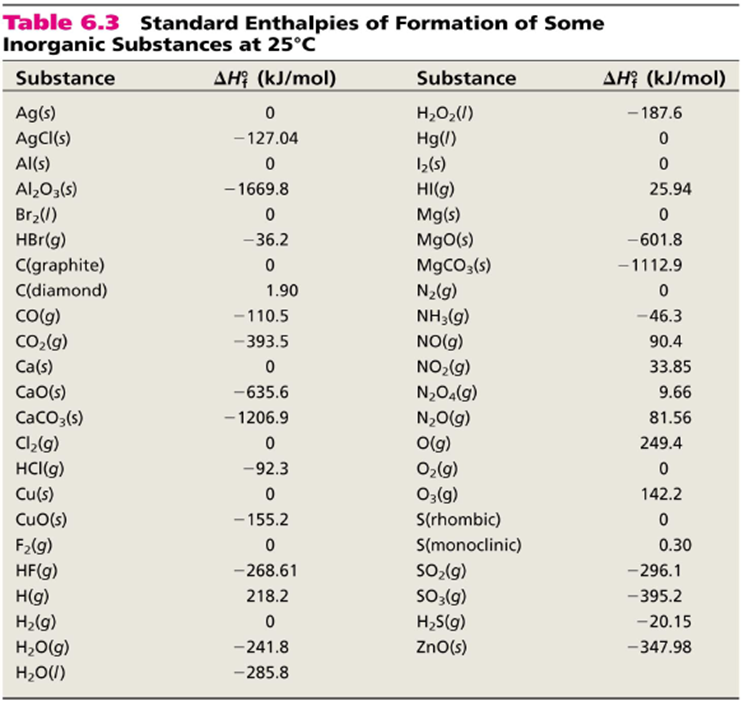
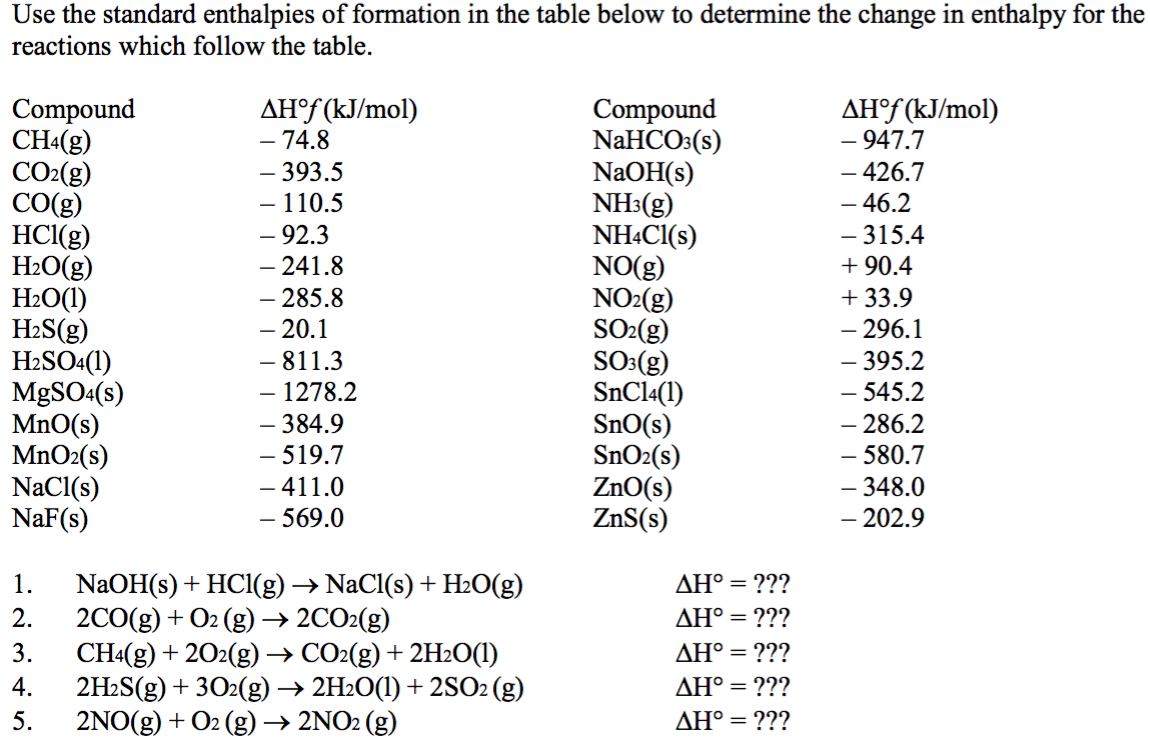
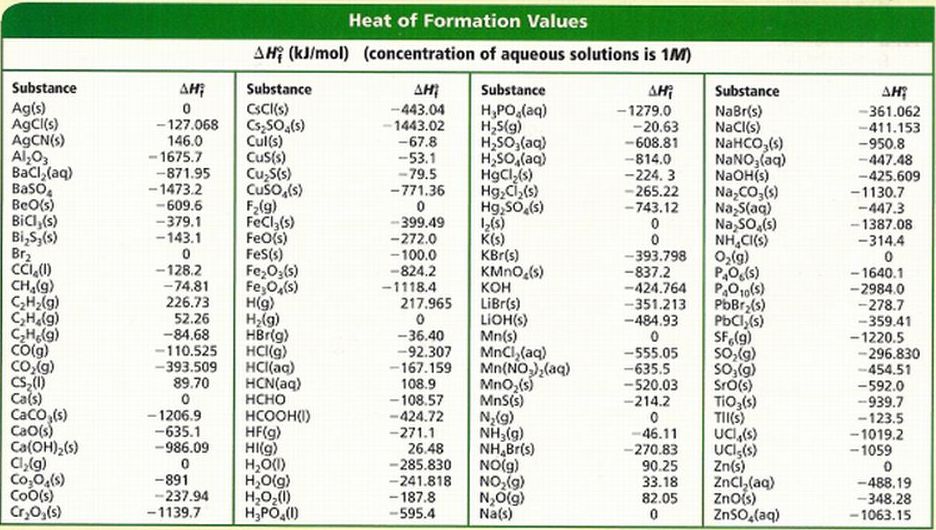
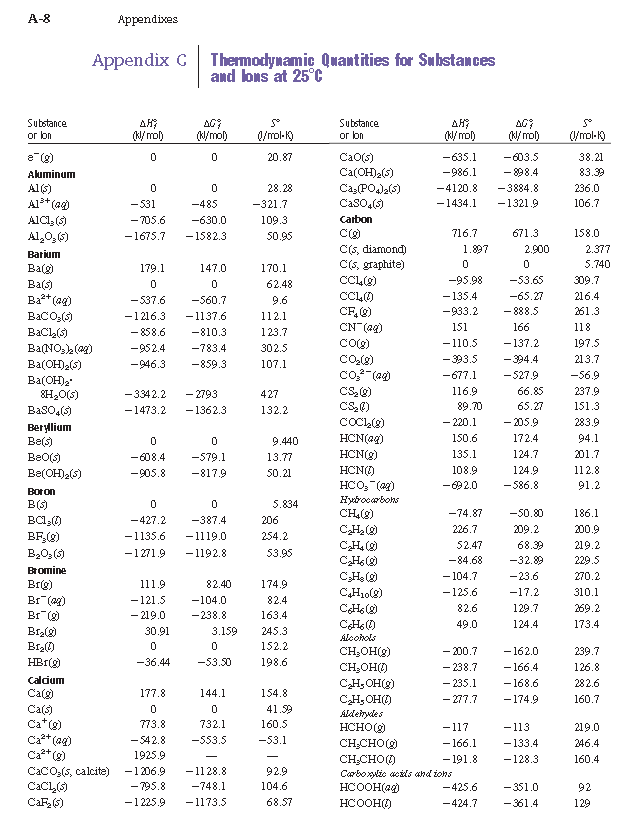
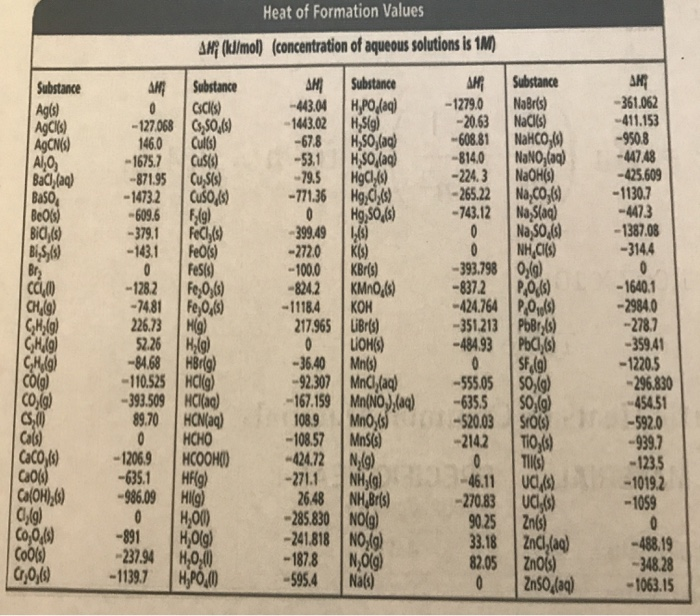
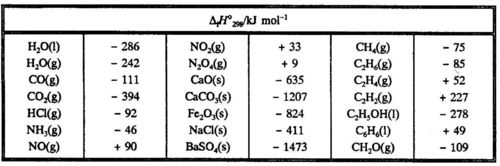
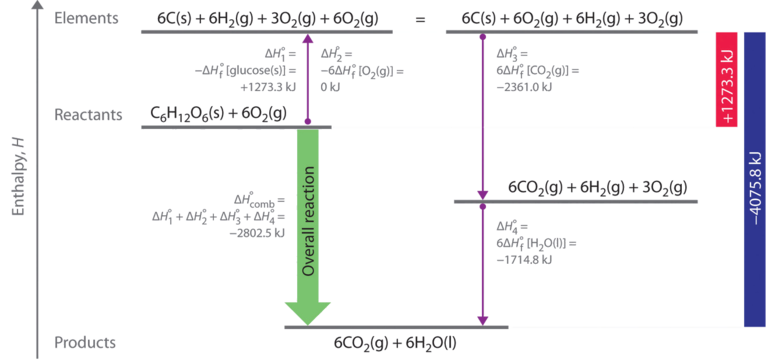
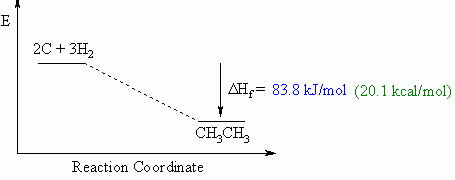
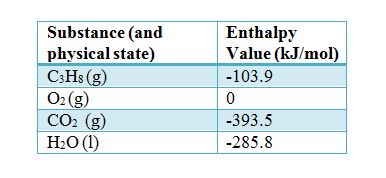
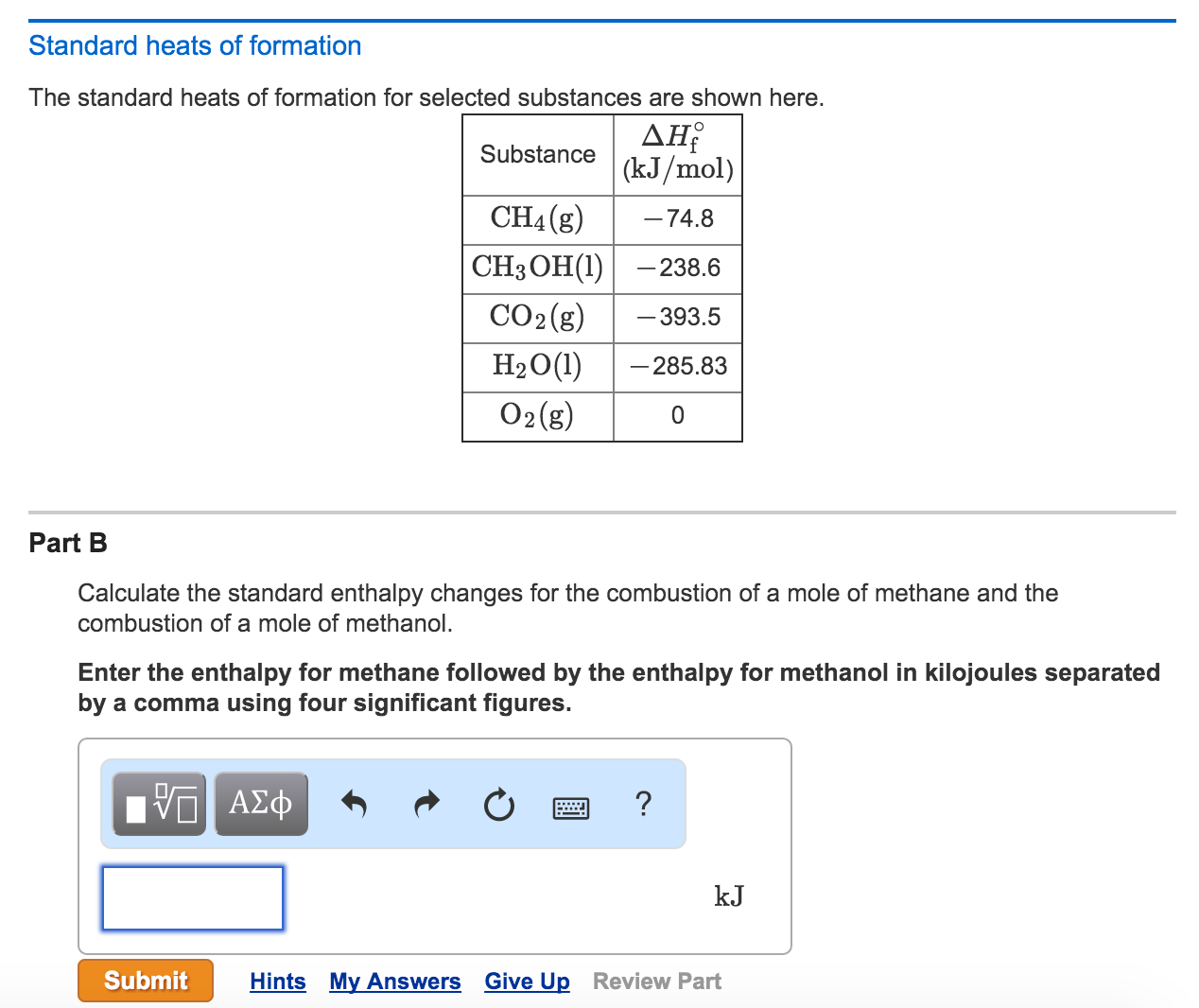
Heats Of Formation Chart

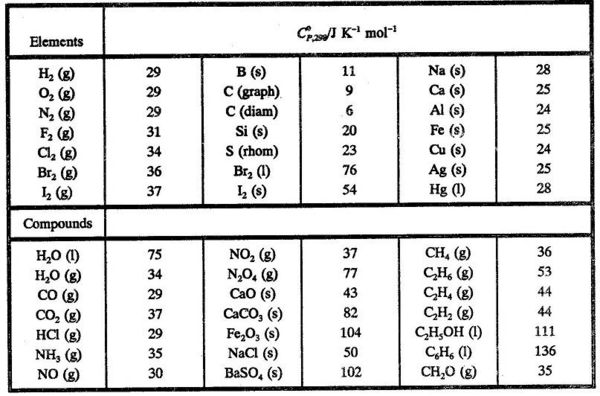
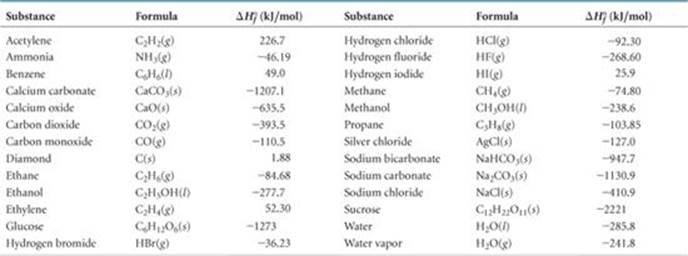
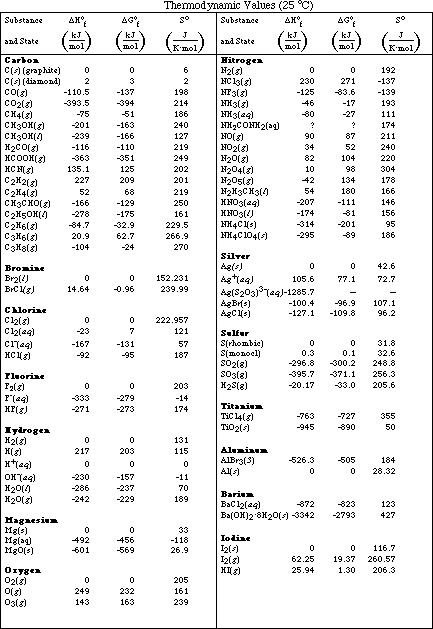
Heats of formation of compounds at 298k from elements in their standard states.
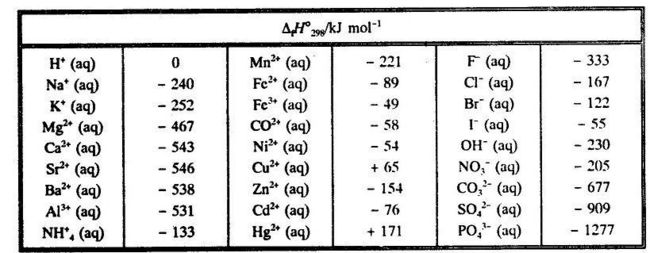
Heats of formation chart. Substance kj mol substance kj mol al 2 o 3 s 1669 8. Br 2 g 30 91. Na aq sodium ion 57 28.
The standard heat of formation is the enthalpy change associated with the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard states. 298 k represented by the symbol δ fh. Standand enthalpies of formation standard entropies of common compounds substance state h f s kj mol j mol k ag s 0 42 6 ag aq 105 79 72 7 agcl s 127 01 96 2 agbr s 100 4 107 1 agno 3 s 124 4 140 9 al s 0 28 3 al 3 aq 538 4 321 7 alcl 3 s 704 110 7 al 2o 3 s 1675 7 50 9 ba s 0 62 8 bacl 2 s 858 6 123 7 baco 3.
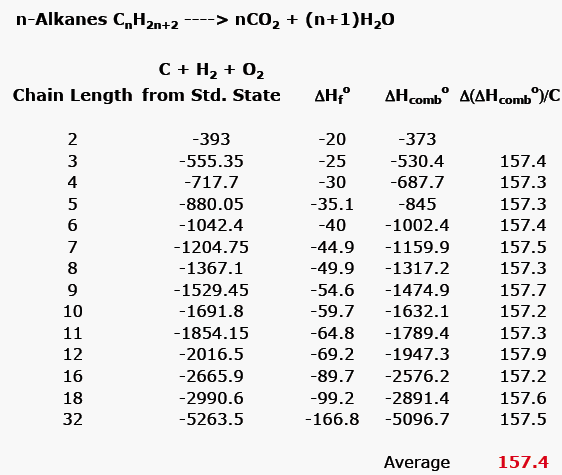
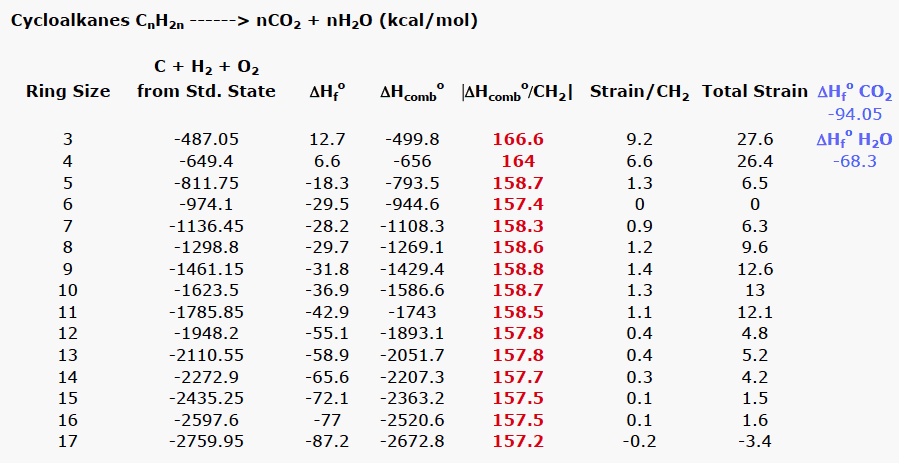
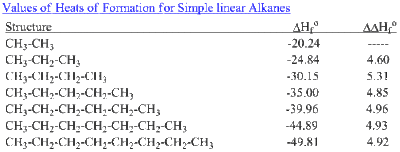
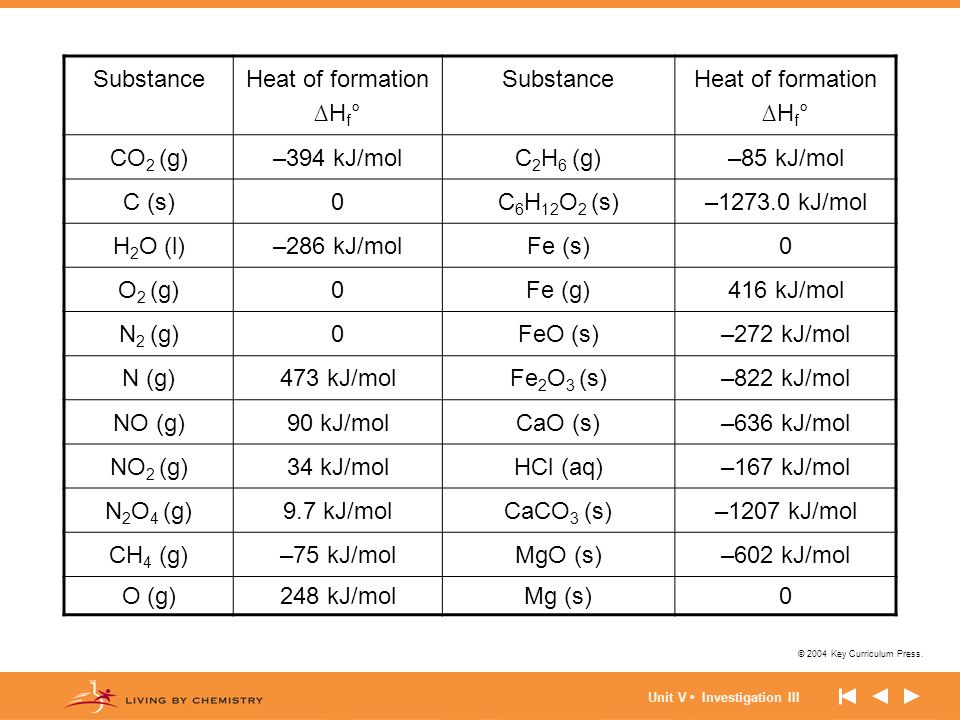
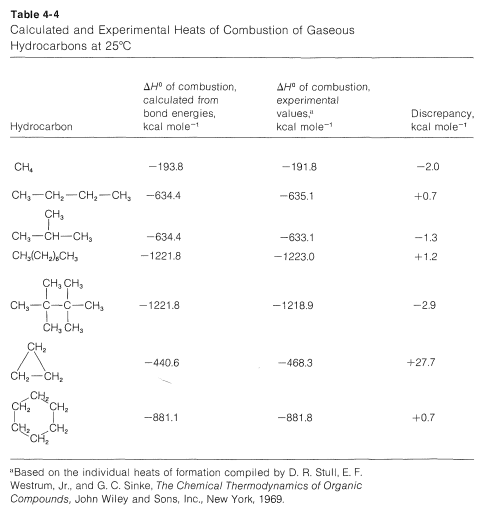
Note that the table for alkanes contains δ f h o values in kcal mol 1 kcal mol 4 184 kj mol and the table for miscellaneous compounds and elements contains these values in kj mol. Standard enthalpy of formation for various compounds compound δh f kj mol compound δh f kj mol compound δh f kj mol compound δh f kj mol ag 2o s 30 6 c 2h 5oh l 277 6 hcl g 92 3 nh 4cl s 315 4 ag 2s s 31 8 c 2h 6 g 84 7 hf g 268 6 nh 4no 3 s 365 1 agbr s 99 5 c 3h 8 g 103 8 hgo s 90 7 nio s 244 3. Nai s sodium iodide 68 84.
C s diamond 1 90. D h o 298 kcal mol 1 h aq proton. No 2 g 33 85.
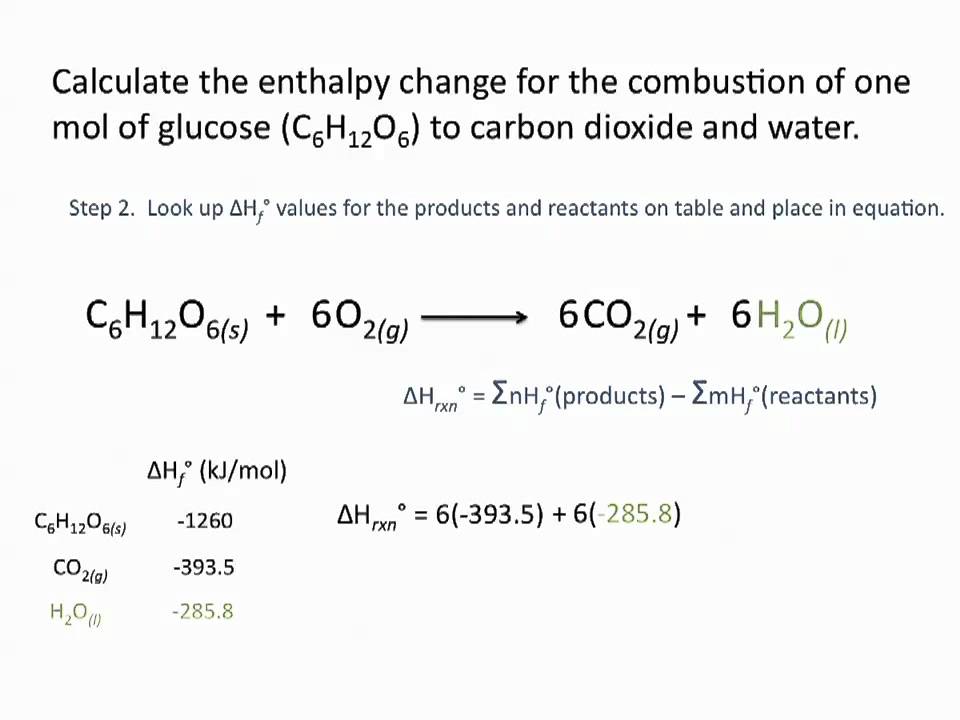
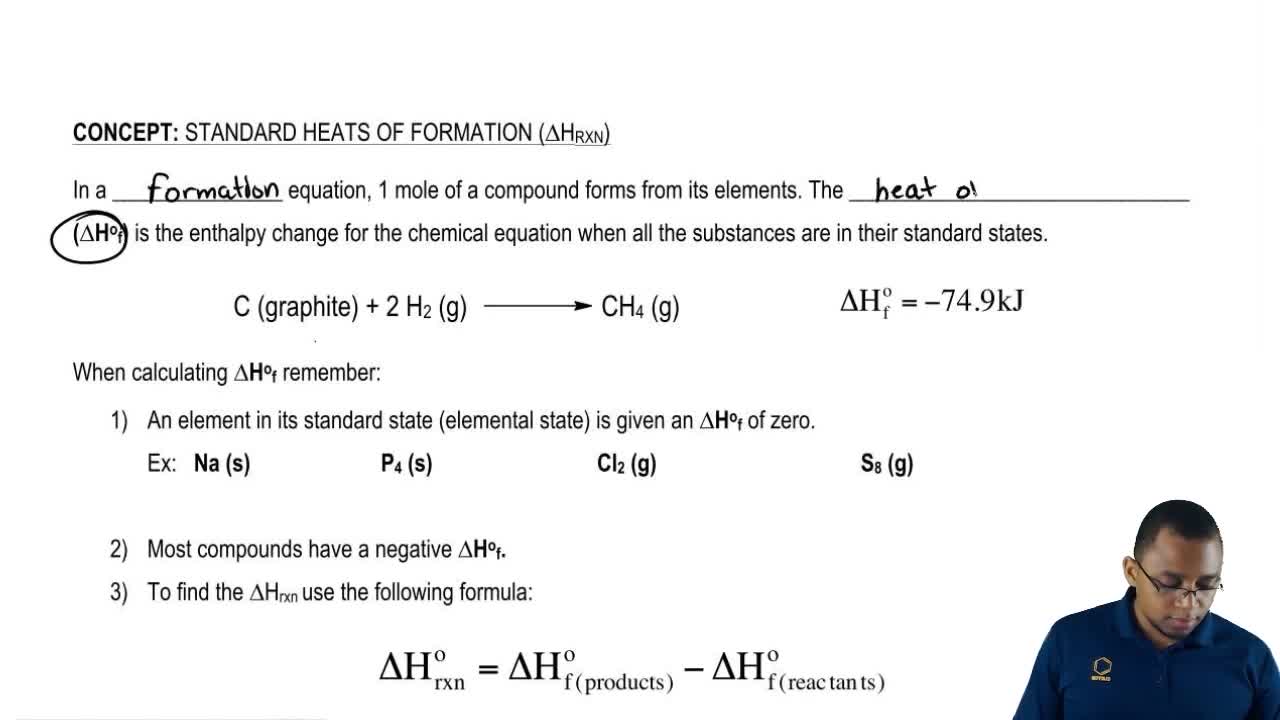
The molar heat of formation or standard enthalpy of formation is the change in enthalpy when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its elements under standard state conditions the standard enthalpy change of formation is the sum of the heats of formation of the products of a reaction minus the sum of the heats of formation of the reactants. Also called standard enthalpy of formation the molar heat of formation of a compound δh f is equal to its enthalpy change δh when one mole of a compound is formed at 25 degrees celsius and one atom from elements in their stable form. Therefore the standard state of an element is its state at 25 c and 101 3 kpa.
C s graphite 0. H 2 o 2 l 187 6. C 2 h 5 oh l 276 98.
These tables include heat of formation data gathered from a variety of sources including the primary and secondary literature as well as the nist chemistry webbook. Since the pressure of the standard formation reaction is fixed at 1 bar the standard formation enthalpy or reaction heat is a function of temperature. Standard heats and free energies of formation and absolute entropies of elements and inorganic compounds.
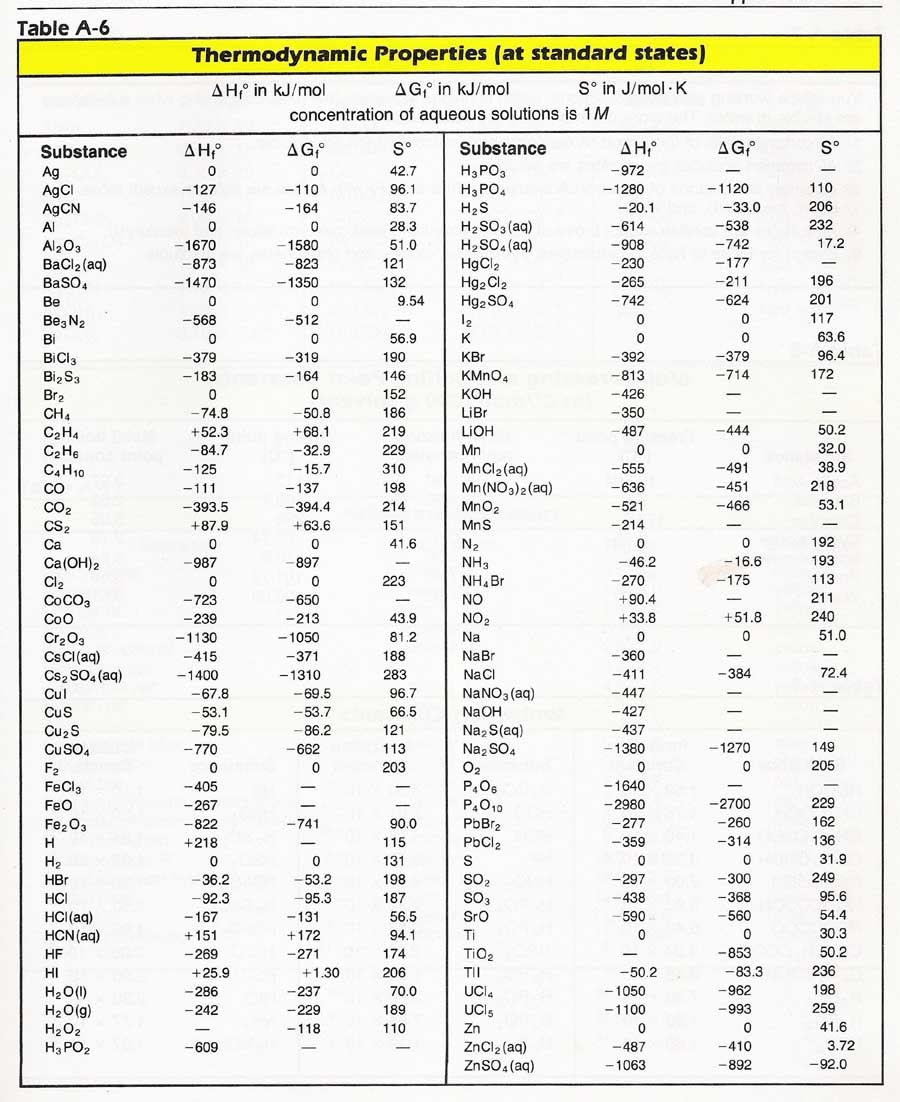
For tabulation purposes standard formation enthalpies are all given at a single temperature. Standard heats of formation of selected substances.